If you were to assess how great a pitcher in baseball truly is, you might find yourself looking at a lot of statistics, most notably ERA or earned run average. With the goal of striking out every batter who steps into the box, pitchers must not only possess elite skill and talent, but also the ability to generate an incredible amount of power. That power is repeated roughly one hundred times per game.
Across sports, very few athletes are required to produce such high levels of force as frequently as baseball pitchers. When athletes specialize as pitchers at a young age and play across multiple teams each year, the volume of throwing and cumulative stress placed on the elbow and surrounding structures can take a serious toll. For a long time, this was believed to threaten a player’s future in the sport.
These issues often begin as lower level conditions such as Little League Elbow, which is typically the result of inadequate rest between pitching outings, or acute bursitis, which involves inflammation of a localized fat pad. Over time, the elbow must repeatedly absorb tremendous force across seasons. This repetitive overhead throwing stresses the tendons and ligaments responsible for elbow stability and increases the risk of more serious injuries, including damage to the ulnar collateral ligament.
As UCL injuries have become increasingly common in younger athletes over the past several years, organizations such as the American Sports Medicine Institute, USA Baseball, Little League Baseball, and Major League Baseball have implemented pitch count guidelines in an effort to protect developing players.
Despite these efforts, higher level athletes continue to face significant risk.
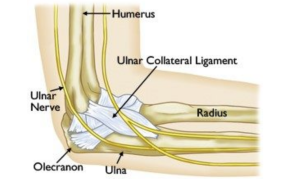
The Ulnar Collateral ligament (UCL) injury
The ulnar collateral ligament is one of the most commonly injured ligaments in repetitive overhead and throwing athletes. To tolerate the high forces required to throw a baseball sixty feet, the ligament gradually stretches and elongates. Eventually, it may no longer be able to maintain the structural integrity of the elbow.
Like most ligament injuries, UCL damage exists on a spectrum. Injuries can range from a mild sprain with inflammation to a complete tear that compromises elbow stability.
UCL Symptoms Include:
- Pain with throwing or inside of the elbow
- Instability
- Decreased strength or power in throwing
- Increased sensitivity around the ulnar nerve “funny bone” causing numbness and tingling in the ring and pinky finger
Diagnosis and Treatment
A UCL injury is diagnosed based on a combination of clinical presentation, physical examination findings, and diagnostic imaging such as X-ray or MRI. The next steps depend on the severity of the injury, healing potential, inflammation levels, and response to rehabilitation.
Further assessment by a physical therapist or athletic trainer is often necessary to determine whether throwing mechanics, body positioning, sequencing, or compensatory strategies are placing excessive stress on the elbow. In many cases, limitations in shoulder mobility prevent a pitcher from generating force efficiently. When this happens, the body looks for power elsewhere.
That power often comes from the inside of the elbow.
Normal pitching mechanics already place approximately 300 newtons, or about 67 pounds, of torque on the inside of the elbow. Now imagine how much additional stress accumulates when mechanics are inefficient and that load is repeated one hundred pitches per game over the course of an entire season.
Tommy John and His Influence
Named after former Los Angeles Dodgers pitcher Tommy John, this surgical procedure has dramatically changed the outlook for throwing athletes. Once considered a career ending injury, UCL reconstruction is now a well established option for athletes who fail conservative treatment.
Tommy John surgery involves replacing the damaged UCL with a tendon graft, often taken from the forearm or hamstring. This is followed by an extensive rehabilitation process that progresses through multiple phases and typically lasts between six and twelve months.
What was once viewed as the end of a pitching career is now often seen as a pathway back to competitive play. Today, UCL reconstruction is commonly performed and heavily emphasized in rehabilitation and sports medicine education.
If you have questions about UCL injuries, Tommy John surgery, or elbow pain related to throwing, consult your primary care physician or visit Next Level Physical Therapy. We are always happy to discuss your concerns and help guide you in the right direction.